「HTMLとJavaScriptで電卓作ってみたいけど、手順が分からない…」
そんなあなたに向けて、今回はAI「Windsurf」にお願いして、電卓アプリを作ってもらいました!
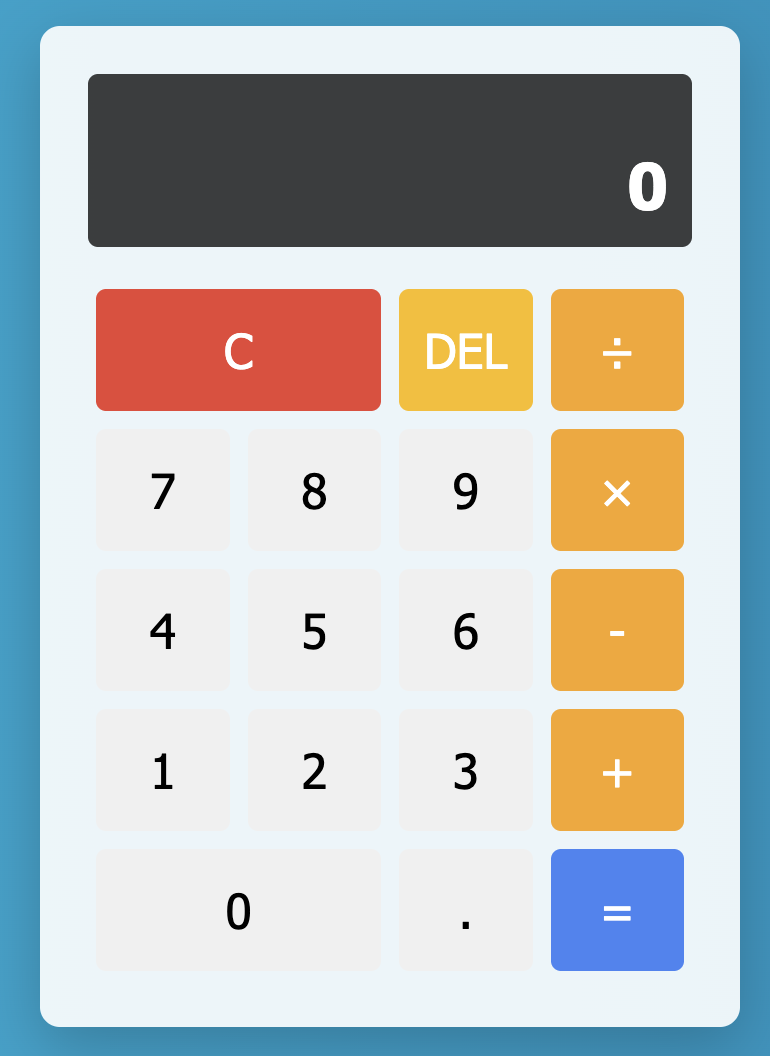
→完成したアプリはこちら。
数字と演算子のボタン、結果表示、デリートやリセット機能も揃った、しっかり使える計算機が完成しました。
この記事では、完成したアプリの中身や、実際に使ったプロンプト、コードのポイントまで、分かりやすくご紹介します!
モダンで機能的なWeb電卓
今回Windsurfが生成したのは、以下3つのファイルで構成された電卓アプリです。
index.html:HTMLで構造を定義styles.css:CSSでデザインを整えるscript.js:JavaScriptでロジックを構築
主な機能はこちら👇
- 数字と演算子(+、−、×、÷)の入力
=ボタンで計算実行Cで全クリア、DELで一文字削除- キーボード操作にも対応(!)
- 直感的でモダンなデザイン
単なる「見た目だけの電卓」ではなく、演算の状態管理や誤操作対策までしっかりしていて、実用レベルの仕上がりです。
使用プロンプトの紹介
Windsurfに投げたプロンプトは以下の通りです。
Create a simple calculator web app using HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
The app should have buttons for numbers 0-9, operations (+, -, ×, ÷), a clear button (C), and an equals button (=).
Display the input and result at the top.
Use modern and clean styling.驚いたことに、これだけの指示で構造、見た目、動きのすべてを整えた3ファイルを出力してくれました…!AIすごい。
役割ごとにポイント解説
index.html:ボタン配置もきれいに設計
コード全文
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Modern Calculator</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="styles.css">
</head>
<body>
<div class="calculator">
<div class="display">
<div class="previous-operand" id="previous-operand"></div>
<div class="current-operand" id="current-operand">0</div>
</div>
<button class="span-two" id="clear">C</button>
<button id="delete">DEL</button>
<button class="operator" id="divide">÷</button>
<button class="number" id="seven">7</button>
<button class="number" id="eight">8</button>
<button class="number" id="nine">9</button>
<button class="operator" id="multiply">×</button>
<button class="number" id="four">4</button>
<button class="number" id="five">5</button>
<button class="number" id="six">6</button>
<button class="operator" id="subtract">-</button>
<button class="number" id="one">1</button>
<button class="number" id="two">2</button>
<button class="number" id="three">3</button>
<button class="operator" id="add">+</button>
<button class="number span-two" id="zero">0</button>
<button class="number" id="decimal">.</button>
<button class="equals" id="equals">=</button>
</div>
<script src="script.js"></script>
</body>
</html><div class="display">
<div class="previous-operand" id="previous-operand"></div>
<div class="current-operand" id="current-operand">0</div>
</div>ここが「式の途中経過」や「現在の数字」を表示する部分です。
ボタンもすべて <button> タグで作られており、読みやすい構造になっています。
styles.css:視認性バツグンのUIデザイン
コード全文
*, *::before, *::after {
box-sizing: border-box;
font-family: 'Segoe UI', Tahoma, Geneva, Verdana, sans-serif;
font-weight: normal;
}
body {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
background: linear-gradient(to right, #00b4db, #0083b0);
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
min-height: 100vh;
}
.calculator {
background-color: rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.9);
border-radius: 10px;
box-shadow: 0 10px 30px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.2);
width: 350px;
max-width: 90vw;
overflow: hidden;
display: grid;
grid-template-columns: repeat(4, 1fr);
grid-gap: 1px;
padding: 1.5rem;
}
.display {
grid-column: 1 / -1;
background-color: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.75);
color: white;
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
align-items: flex-end;
justify-content: space-around;
padding: 0.75rem;
word-wrap: break-word;
word-break: break-all;
text-align: right;
margin-bottom: 1rem;
border-radius: 5px;
min-height: 80px;
}
.previous-operand {
color: rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.75);
font-size: 1.2rem;
min-height: 1.5rem;
}
.current-operand {
color: white;
font-size: 2rem;
font-weight: bold;
}
button {
cursor: pointer;
font-size: 1.5rem;
border: none;
outline: none;
background-color: #f0f0f0;
margin: 0.25rem;
padding: 1rem 0;
border-radius: 5px;
transition: all 0.2s;
}
button:hover {
background-color: #dcdcdc;
}
button:active {
background-color: #cccccc;
transform: translateY(2px);
}
.span-two {
grid-column: span 2;
}
.operator {
background-color: #f8a51d;
color: white;
}
.operator:hover {
background-color: #e5951a;
}
.equals {
background-color: #4285f4;
color: white;
}
.equals:hover {
background-color: #3b77db;
}
#clear {
background-color: #ea4335;
color: white;
}
#clear:hover {
background-color: #d03c2f;
}
#delete {
background-color: #fbbc05;
color: white;
}
#delete:hover {
background-color: #e2a904;
}.calculator {
background-color: rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.9);
box-shadow: 0 10px 30px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.2);
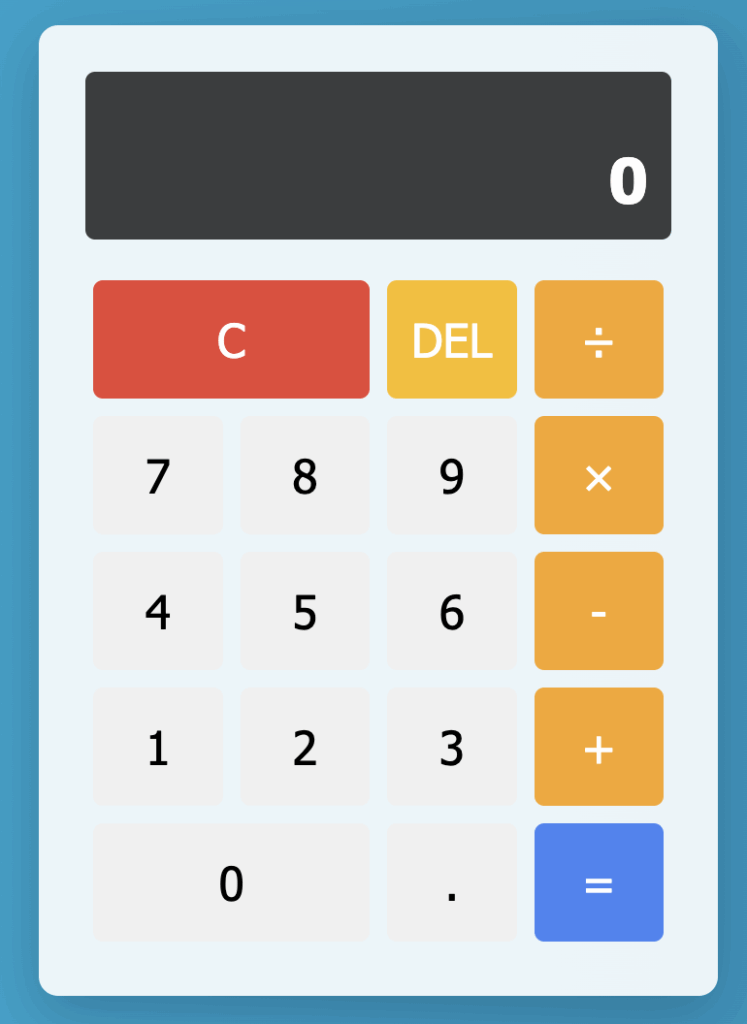
}電卓本体はガラスっぽい白背景、ボタンは色分けされていて、
「Cは赤」「=は青」「演算子はオレンジ」と、誰でも直感的に操作できます。
script.js:ロジックはクラス設計で整理
コード全文
class Calculator {
constructor(previousOperandElement, currentOperandElement) {
this.previousOperandElement = previousOperandElement;
this.currentOperandElement = currentOperandElement;
this.clear();
}
clear() {
this.currentOperand = '0';
this.previousOperand = '';
this.operation = undefined;
}
delete() {
if (this.currentOperand === '0') return;
this.currentOperand = this.currentOperand.toString().slice(0, -1);
if (this.currentOperand === '') this.currentOperand = '0';
}
appendNumber(number) {
if (number === '.' && this.currentOperand.includes('.')) return;
if (this.currentOperand === '0' && number !== '.') {
this.currentOperand = number;
} else {
this.currentOperand = this.currentOperand.toString() + number;
}
}
chooseOperation(operation) {
if (this.currentOperand === '0') return;
if (this.previousOperand !== '') {
this.compute();
}
this.operation = operation;
this.previousOperand = this.currentOperand;
this.currentOperand = '0';
}
compute() {
let computation;
const prev = parseFloat(this.previousOperand);
const current = parseFloat(this.currentOperand);
if (isNaN(prev) || isNaN(current)) return;
switch (this.operation) {
case '+':
computation = prev + current;
break;
case '-':
computation = prev - current;
break;
case '×':
computation = prev * current;
break;
case '÷':
if (current === 0) {
this.currentOperand = 'Error';
this.operation = undefined;
this.previousOperand = '';
return;
}
computation = prev / current;
break;
default:
return;
}
this.currentOperand = computation.toString();
this.operation = undefined;
this.previousOperand = '';
}
getDisplayNumber(number) {
if (number === 'Error') return 'Error';
const stringNumber = number.toString();
const integerDigits = parseFloat(stringNumber.split('.')[0]);
const decimalDigits = stringNumber.split('.')[1];
let integerDisplay;
if (isNaN(integerDigits)) {
integerDisplay = '';
} else {
integerDisplay = integerDigits.toLocaleString('en', { maximumFractionDigits: 0 });
}
if (decimalDigits != null) {
return `${integerDisplay}.${decimalDigits}`;
} else {
return integerDisplay;
}
}
updateDisplay() {
this.currentOperandElement.innerText = this.getDisplayNumber(this.currentOperand);
if (this.operation != null) {
this.previousOperandElement.innerText =
`${this.getDisplayNumber(this.previousOperand)} ${this.operation}`;
} else {
this.previousOperandElement.innerText = '';
}
}
}
// DOM elements
const previousOperandElement = document.getElementById('previous-operand');
const currentOperandElement = document.getElementById('current-operand');
const numberButtons = document.querySelectorAll('.number');
const operationButtons = document.querySelectorAll('.operator');
const equalsButton = document.getElementById('equals');
const clearButton = document.getElementById('clear');
const deleteButton = document.getElementById('delete');
// Create calculator instance
const calculator = new Calculator(previousOperandElement, currentOperandElement);
// Event listeners for number buttons
numberButtons.forEach(button => {
button.addEventListener('click', () => {
let number;
if (button.id === 'zero') number = '0';
else if (button.id === 'one') number = '1';
else if (button.id === 'two') number = '2';
else if (button.id === 'three') number = '3';
else if (button.id === 'four') number = '4';
else if (button.id === 'five') number = '5';
else if (button.id === 'six') number = '6';
else if (button.id === 'seven') number = '7';
else if (button.id === 'eight') number = '8';
else if (button.id === 'nine') number = '9';
else if (button.id === 'decimal') number = '.';
calculator.appendNumber(number);
calculator.updateDisplay();
});
});
// Event listeners for operation buttons
operationButtons.forEach(button => {
button.addEventListener('click', () => {
let operation;
if (button.id === 'add') operation = '+';
else if (button.id === 'subtract') operation = '-';
else if (button.id === 'multiply') operation = '×';
else if (button.id === 'divide') operation = '÷';
calculator.chooseOperation(operation);
calculator.updateDisplay();
});
});
// Event listener for equals button
equalsButton.addEventListener('click', () => {
calculator.compute();
calculator.updateDisplay();
});
// Event listener for clear button
clearButton.addEventListener('click', () => {
calculator.clear();
calculator.updateDisplay();
});
// Event listener for delete button
deleteButton.addEventListener('click', () => {
calculator.delete();
calculator.updateDisplay();
});
// Keyboard support
document.addEventListener('keydown', event => {
if (event.key >= '0' && event.key <= '9') {
const numberMap = {
'0': 'zero', '1': 'one', '2': 'two', '3': 'three', '4': 'four',
'5': 'five', '6': 'six', '7': 'seven', '8': 'eight', '9': 'nine'
};
document.getElementById(numberMap[event.key]).click();
}
if (event.key === '.') document.getElementById('decimal').click();
if (event.key === '+') document.getElementById('add').click();
if (event.key === '-') document.getElementById('subtract').click();
if (event.key === '*') document.getElementById('multiply').click();
if (event.key === '/') {
event.preventDefault();
document.getElementById('divide').click();
}
if (event.key === 'Enter' || event.key === '=') document.getElementById('equals').click();
if (event.key === 'Escape') document.getElementById('clear').click();
if (event.key === 'Backspace') document.getElementById('delete').click();
});class Calculator {
appendNumber(number) { ... }
chooseOperation(operation) { ... }
compute() { ... }
updateDisplay() { ... }
}操作ロジックは Calculator クラスとして定義。
値の追加・演算子の選択・計算実行などがすべて関数に整理されていて、読みやすい設計になっています。
さらに、keyboard support も実装されており、数字や + をキーボードで打ってもちゃんと反応します!
JavaScript初学者でも「オブジェクト指向ってこうやって使うんだ!」という学びが得られる構成です。
Windsurfで電卓を作ってみて感じたこと
今回の電卓アプリは、見た目も中身もバランスのとれた仕上がりでした。「ちょっと使えるレベルのアプリ」を、ここまで短時間で作れるのは本当に魅力です。
コードのクオリティも高く、そのまま学習教材としても使える内容になっているので、「何か作ってみたい」初心者にはピッタリ。
今後は履歴機能付き電卓や、関数電卓への拡張なども面白そうですね!
「AIって本当にコード書けるの?」と思っている方こそ、ぜひWindsurfで電卓作りから始めてみてください。